Reduced risk of distant recurrence
In the NATALEE trial, KISQALI + AI reduced the threat of recurrence with incurable metastatic disease in the broadest population of patients with stage II/III HR+/HER2- eBC at high risk of recurrence.
In patients with stage II/III HR+/HER2- eBC,
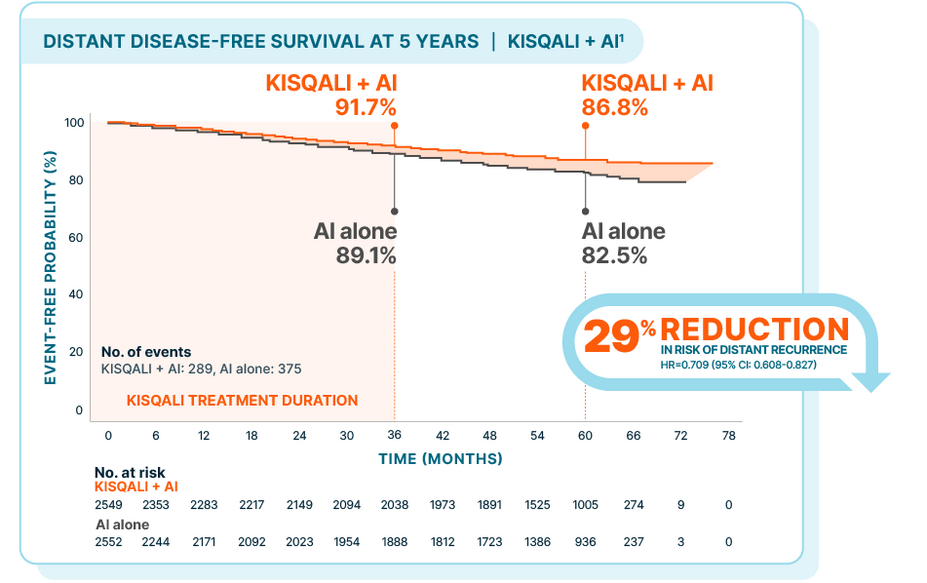
Over 5 years, KISQALI showed a 29% reduction in the risk of distant recurrence
The DDFS benefit was consistent with iDFS and increased over time with KISQALI + AI, beyond the treatment period
NATALEE: KISQALI + AI vs AI alone
At a median follow-up of 55.5 months
Hazard ratio is based on stratified Cox model.2
DDFS was defined as the time from randomization to the date of the first event of distant recurrence, second primary non-breast invasive cancer (excluding basal and squamous cell carcinomas of the skin), or death (any cause).2
In the 5-year prespecified analysis1:
At 3 years: 2.6% absolute difference
At 5 years: 4.3% absolute difference
At the time of data cutoff, only 11.3% of patients receiving KISQALI + AI had experienced a DDFS event vs 14.7% of patients treated with AI alone
The 5-year analysis was prespecified and observational in nature; as such, there was no prespecified statistical procedure controlling for type 1 error
NATALEE was a randomized, multicenter, open-label, phase III study of KISQALI + letrozole or anastrozole (n=2549) vs letrozole or anastrozole (n=2552) for the adjuvant treatment of men and women with stage II/III HR+/HER2- eBC, including all those with node-positive or high-risk node-negative disease (eligible stages and nodal status include: anatomic stage group IIB-III, or anatomic stage group IIA that is either node positive, or node negative with histologic grade 3, or histologic grade 2 with Ki-67 ≥20% and/or high risk by gene signature testing). iDFS was the primary end point; DDFS was a secondary end point. At a median follow-up of 33.3 months, with 509 iDFS events in the study (226 [8.9%] in the KISQALI arm and 283 [11.1%] in the NSAI-alone arm), iDFS at the 3-year landmark was 90.7% for KISQALI + NSAI vs 87.6% for NSAI alone (absolute difference 3.1%); there was a 25.1% relative reduction in the risk of an iDFS event; HR=0.749 (95% CI: 0.628-0.892).3-5