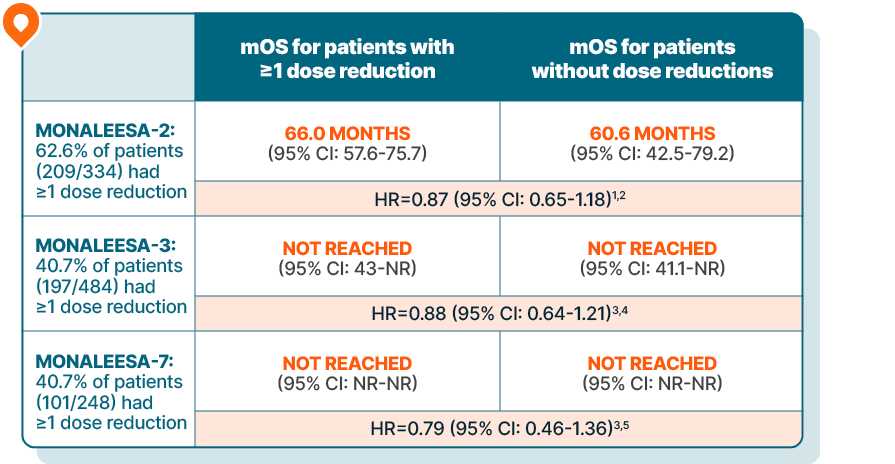
KISQALI maintained overall survival in patients requiring dose reductions across 3 phase III trials
DOSE REDUCTION DATA
Lowering the dose of KISQALI can help address side effects and, in clinical studies, did not impact efficacy1-5
Time-varying Cox regression analysis of OS by dose reduction
Results are based on a post hoc analysis; efficacy in the placebo comparator arms was not assessed and should be interpreted with caution

In MONALEESA-2, managing adverse reactions with dose reductions helped patients stay on therapy an average of 6.5 months longer than those without dose reductions.2
MONALEESA-2 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III study of KISQALI + letrozole (n=334) vs placebo + letrozole (n=334) in postmenopausal patients with HR+/HER2- mBC who received no prior therapy for advanced disease. OS was a secondary end point; PFS was the primary end point. At a median follow-up of 80 months, mOS was 63.9 months with KISQALI + letrozole (95% CI: 52.4-71.0) vs 51.4 months with placebo + letrozole (95% CI: 47.2-59.7); HR=0.765 (95% CI: 0.628-0.932); P=0.004.6-8
MONALEESA-3 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III study of KISQALI + fulvestrant (n=484) vs placebo + fulvestrant (n=242) in postmenopausal patients with HR+/HER2- mBC who received no or only 1 line of prior ET for advanced disease. OS was a secondary end point; PFS was the primary end point. In an exploratory analysis of a 1L subgroup of patients receiving KISQALI + fulvestrant (n=237) or placebo + fulvestrant (n=128), at a median follow-up of 71 months mOS was 67.6 months with KISQALI + fulvestrant (95% CI: 59.6-NR) vs 51.8 months with placebo + fulvestrant (95% CI: 40.4-61.2); HR=0.673 (95% CI: 0.504-0.899). At a median follow-up of 39 months, statistical significance was established for overall survival in the ITT population; HR=0.724 (95% CI: 0.568-0.924); P=0.00455. Results from the 71-month analysis were not prespecified and were observational in nature; as such, there was no prespecified statistical procedure controlling for type 1 error.6,9-11
MONALEESA-7 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III study of KISQALI + ET (NSAI or tamoxifen) + goserelin (n=335) vs placebo + ET (NSAI or tamoxifen) + goserelin (n=337) (ITT) in premenopausal patients with HR+/HER2- mBC who received no prior ET for advanced disease. KISQALI is not indicated for concomitant use with tamoxifen. Efficacy results are from a prespecified subgroup analysis of 495 patients who received KISQALI (n=248) or placebo (n=247) with an NSAI + goserelin and were not powered to show statistical significance. OS was a secondary end point; PFS was the primary end point. At a median follow-up of 54 months (exploratory analysis), mOS was 58.7 months with KISQALI + NSAI + goserelin (95% CI: 48.5-NR) vs 47.7 months with placebo + NSAI + goserelin (95% CI: 41.2-55.4); HR=0.798 (95% CI: 0.615-1.035). At a median follow-up of 35 months, statistical significance was established for overall survival in the ITT population; HR=0.71 (95% CI: 0.54-0.95); P=0.00973. Results from the 54-month analysis were not prespecified and were observational in nature; as such, there was no prespecified statistical procedure controlling for type 1 error.6,12-15
1L, first line; ET, endocrine therapy; HER2-, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative; HR, hazard ratio; HR+, hormone receptor-positive; ITT, intent to treat; mBC, metastatic breast cancer; mOS, median overall survival; NR, not reached; NSAI, nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor; OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival.
EXPERT VIDEO
Expert perspective on dosing and patient adherence in HR+/HER2- mBC
Dr Nick McAndrew shares his perspective on simple dose reductions with KISQALI and how to improve adherence in patients with HR+/HER2- mBC.
Dr McAndrew has been compensated for his time by Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation.
KISQALI Treatment Guide
AI, aromatase inhibitor.