PK/PD data
KISQALI—a different CDK4/6 inhibitor
CDK4 is a key driver of HR+/HER2- mBC
CDK4 plays a critical role in breast cancer cell cycle progression and cell proliferation1
Levels of CDK4 are increased in many breast tumors while levels of CDK6 are decreased2-4
Inhibition of CDK4 has been shown to reduce cell proliferation in breast cancer tumors1
Available drug is able to penetrate cells to bind and inhibit CDK45,6
Available drug is the concentration of drug that is able to reach the bloodstream for circulation
All CDK4/6 inhibitors are different
Data derived from 2 separate publications6,7
Select differences among CDK4/6 inhibitors6-10
KISQALI has been shown to prolong the QT interval in a concentration-dependent manner. Please see Warning/Precaution on QT interval prolongation.1
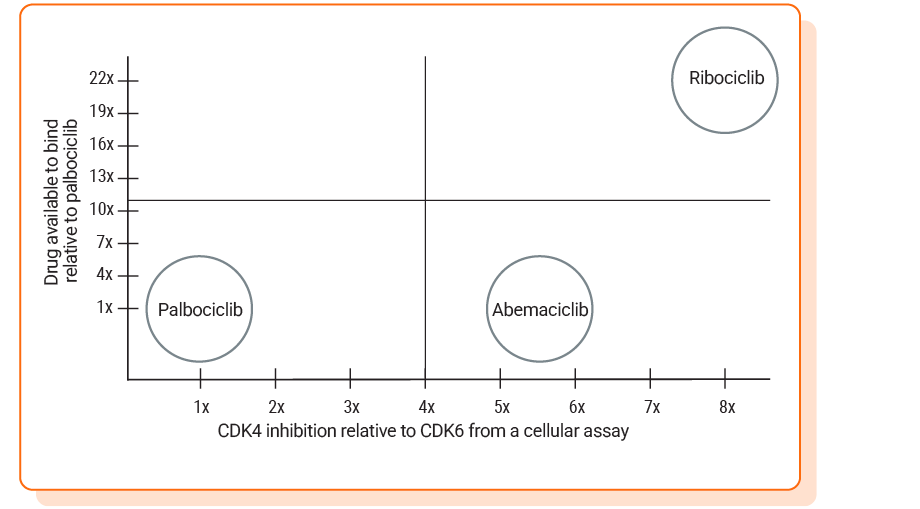
Ribociclib inhibits CDK4 up to 8x more than CDK66,7
Relative inhibition of CDK4 to CDK6 was reported from 2 separate publications. The relative inhibition in the cellular assay was 8.0-fold for ribociclib, 5.5-fold for abemaciclib, and 1.3-fold for palbociclib.6 In the biochemical assay, affinity for CDK4 vs CDK6 was 5-fold for ribociclib, 9-fold for abemaciclib, and 1-fold for palbociclib7
Inhibition of CDK4 relative to CDK6 in the above chart was based on a preclinical, in vitro cellular assay. The activities of ribociclib, palbociclib, and abemaciclib were tested in proliferation assays using cancer cell lines where either CDK4 or CDK6 plays a dominant role in cell cycle progression6
Ribociclib had high levels of drug available to bind in a pharmacokinetic analysis7-10
Drug available to bind was based on steady-state average unbound drug concentration at doses: ribociclib (600 mg once daily), palbociclib (125 mg once daily), and abemaciclib (200 mg twice daily). Values were normalized to palbociclib. Unbound drug exposure may not correlate with clinical outcomes
The information herein is not presented to compare the efficacy or safety profile of the discussed compounds. No implication of superiority or inferiority is intended or should be inferred, as the data herein do not necessarily correlate with clinical outcomes
This information is being shared with health care professionals to help ensure an accurate understanding of the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic profiles of these products: ribociclib, palbociclib, and abemaciclib; different analyses may yield different results
There have been no head-to-head clinical studies among any of these products: ribociclib, palbociclib, and abemaciclib
This information is derived from publications for the respective products, which are based on presently available data
This information neither conveys, nor attempts to convey, the full benefit-risk profile of each product described. Treatment decisions are made based on a number of different factors related to the disease, patient, and potential therapy under consideration